RCTF 2022 Reverse 复现
picStore(re)
https://impartial-poinsettia-a05.notion.site/Lua-953ca64d37c9478b82d394ea2f2a0ca1#ce05742c1bd04285ba87bf4d398a861cdump 后 用 https://luadec.metaworm.site/在线反编译
-- filename:
-- version: lua53
-- line: [0, 0] id: 0
menu = function()
-- line: [2, 12] id: 1
print("-------------------Pictrue Store System-------------------")
print("1. upload")
print("2. download")
print("3. delete")
print("4. list")
print("5. check")
print("6. exit")
io.write("choice>> ")
end
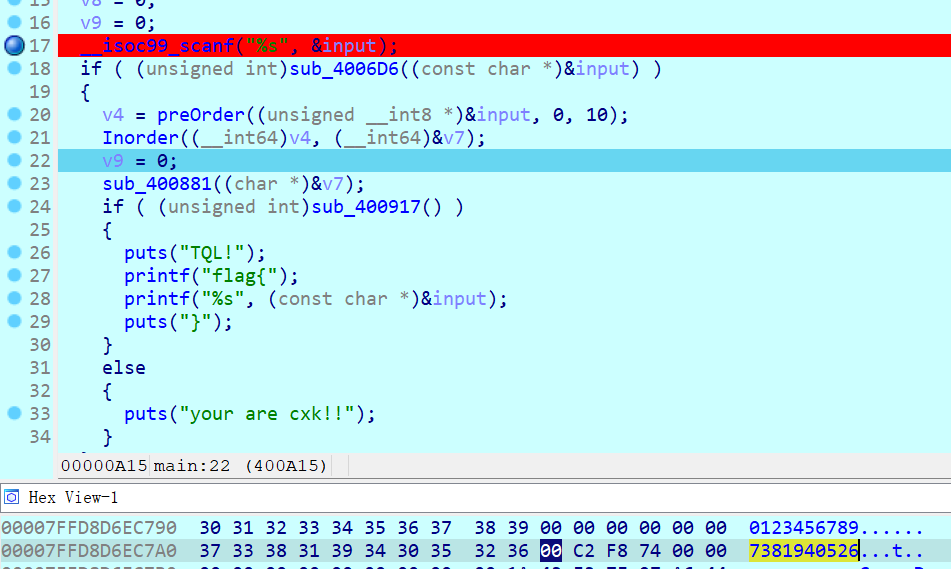
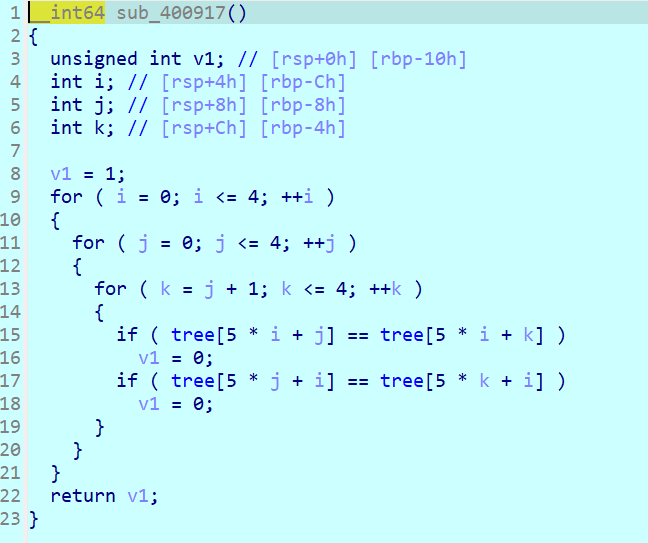
upload_impl = function()
-- line: [14, 21] id: 2
local r0_2 = a_f3_9a7nhRC()
if r0_2 ~= nil then
io.write("img data: ")
a_1sV7zC5yL_(r0_2)
end
end
download_impl = function()
-- line: [23, 31] id: 3
io.write("link: ")
local r0_3 = io.read("*number")
if a_IjKn_GF3FE(r0_3) == 1 then
io.write("img data: ")
a_TUBSK2FAhN(r0_3)
end
end
delete_impl = function()
-- line: [33, 41] id: 4
io.write("link: ")
if a_8jzNK8OZ4i(io.read("*number")) == 0 then
print("error")
end
end
list_impl = function()
-- line: [43, 57] id: 5
print("-------------------img list-------------------")
local r0_5 = 0
local r1_5 = 1
while r0_5 < 30 do
if a_IjKn_GF3FE(r0_5) == 1 then
r1_5 = r1_5 + 1
print(string.format("%d. pic_%04d. link: http://%d\n", r1_5, r0_5, r0_5))
end
r0_5 = r0_5 + 1
end
end
check_impl = function()
-- line: [59, 84] id: 6
local r0_6 = 0
local r1_6 = 0
local r2_6 = ""
local r3_6 = false
while r0_6 < 30 do
local r4_6 = a_IjKn_GF3FE(r0_6)
if r0_6 % 2 == 0 and r4_6 == 1 then
r1_6 = r1_6 + 1
local r5_6 = a_Cc_ClWQsa5(r0_6)
if #r5_6 ~= 2 then
r3_6 = true
end
r2_6 = r2_6 .. r5_6
end
r0_6 = r0_6 + 1
end
if r1_6 == 15 and #r2_6 == 30 and r3_6 == false and check_func(r2_6) == true then
print("now, you know the flag~")
print(r2_6)
else
print("you fail!")
end
end
main_logic = function()
-- line: [86, 108] id: 7
while true do
menu()
local r0_7 = io.read("*l")
if r0_7 == "1" then
upload_impl()
elseif r0_7 == "2" then
download_impl()
elseif r0_7 == "3" then
delete_impl()
elseif r0_7 == "4" then
list_impl()
elseif r0_7 == "5" then
check_impl()
elseif r0_7 == "6" then
print("bye~")
break
else
print("bad choice")
end
end
end
value_list = function(r0_8)
-- line: [111, 118] id: 8
local r1_8 = {}
for r5_8 = 1, string.len(r0_8), 1 do
r1_8[#r1_8 + 1] = string.byte(r0_8, r5_8)
end
return r1_8
end
tobinary = function(r0_9)
-- line: [122, 135] id: 9
local r1_9 = r0_9
local r2_9 = ""
repeat
if r1_9 % 2 == 1 then
local r3_9 = r2_9
r2_9 = r3_9 .. "1"
else
local r3_9 = r2_9
r2_9 = r3_9 .. "0"
end
local r3_9 = math.modf(r1_9 / 2)
r1_9 = r3_9
until r1_9 == 0
return string.reverse(r2_9)
end
xor = function(r0_10, r1_10)
-- line: [137, 170] id: 10
local r2_10 = tobinary(r0_10)
local r3_10 = tobinary(r1_10)
local r4_10 = string.len(r2_10)
local r5_10 = string.len(r3_10)
local r6_10 = 0
local r7_10 = 0
local r8_10 = ""
if r5_10 < r4_10 then
for r12_10 = 1, math.floor(r4_10 - r5_10), 1 do
r3_10 = "0" .. r3_10
end
r6_10 = r4_10
elseif r4_10 < r5_10 then
for r12_10 = 1, math.floor(r5_10 - r4_10), 1 do
r2_10 = "0" .. r2_10
end
r6_10 = r5_10
end
for r12_10 = 1, r6_10, 1 do
if string.sub(r2_10, r12_10, r12_10) == string.sub(r3_10, r12_10, r12_10) then
r8_10 = r8_10 .. "0"
else
r8_10 = r8_10 .. "1"
end
end
return tonumber(r8_10, 2)
end
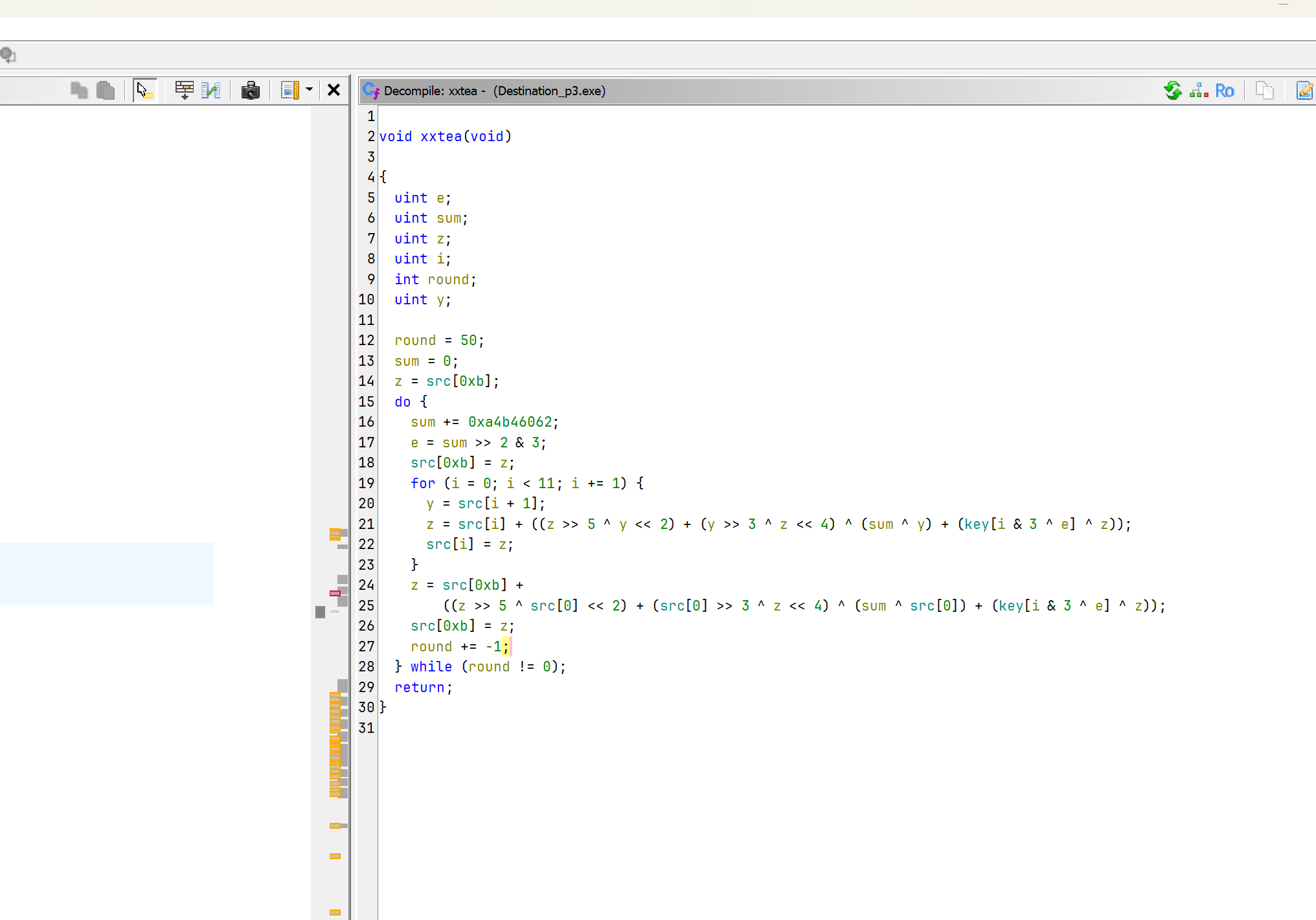
check_func = function(r0_11)
-- line: [172, 195] id: 11
local input = value_list(r0_11)
local r2_11 = {}
local ans = {
105,
244,
63,
10,
24,
169,
248,
107,
129,
138,
25,
182,
96,
176,
14,
89,
56,
229,
206,
19,
23,
21,
22,
198,
179,
167,
152,
66,
28,
201,
213,
80,
162,
151,
102,
36,
91,
37,
50,
17,
170,
41,
3,
84,
85,
226,
131,
38,
71,
32,
18,
142,
70,
39,
112,
220,
16,
219,
159,
222,
11,
119,
99,
203,
47,
148,
185,
55,
93,
48,
153,
113,
1,
237,
35,
75,
67,
155,
161,
74,
108,
76,
181,
233,
186,
44,
125,
232,
88,
8,
95,
163,
200,
249,
120,
243,
174,
212,
252,
234,
58,
101,
228,
86,
109,
144,
104,
121,
117,
87,
15,
132,
12,
20,
165,
115,
136,
135,
118,
69,
68,
2,
82,
123,
250,
251,
53,
255,
51,
221,
211,
195,
145,
140,
254,
0,
116,
43,
29,
217,
197,
183,
168,
188,
34,
218,
146,
147,
98,
149,
246,
180,
103,
33,
40,
207,
208,
192,
143,
26,
154,
225,
100,
141,
175,
124,
230,
62,
177,
205,
110,
202,
253,
173,
46,
52,
114,
164,
166,
137,
158,
122,
13,
83,
178,
133,
189,
187,
7,
184,
77,
245,
216,
190,
194,
72,
157,
172,
171,
199,
160,
45,
49,
27,
204,
81,
6,
92,
59,
209,
239,
130,
97,
61,
214,
215,
73,
90,
126,
42,
30,
240,
79,
224,
78,
223,
111,
60,
4,
5,
196,
231,
106,
64,
139,
235,
150,
227,
238,
191,
127,
31,
156,
54,
241,
242,
134,
247,
128,
65,
94,
57,
210,
236,
9,
193
}
for i = 1, #input, 1 do
input[i] = xor(input[i], i - 1)
input[i] = xor(input[i], 255)
input[i] = input[i] & 255
r2_11[#r2_11 + 1] = ans[input[i] + 1]
end
local r4_11 = a_AHy3JniQH4(r2_11) == 1
end
main = function()
-- line: [198, 201] id: 12
a_bfBfrMZriK()
main_logic()
end
main()
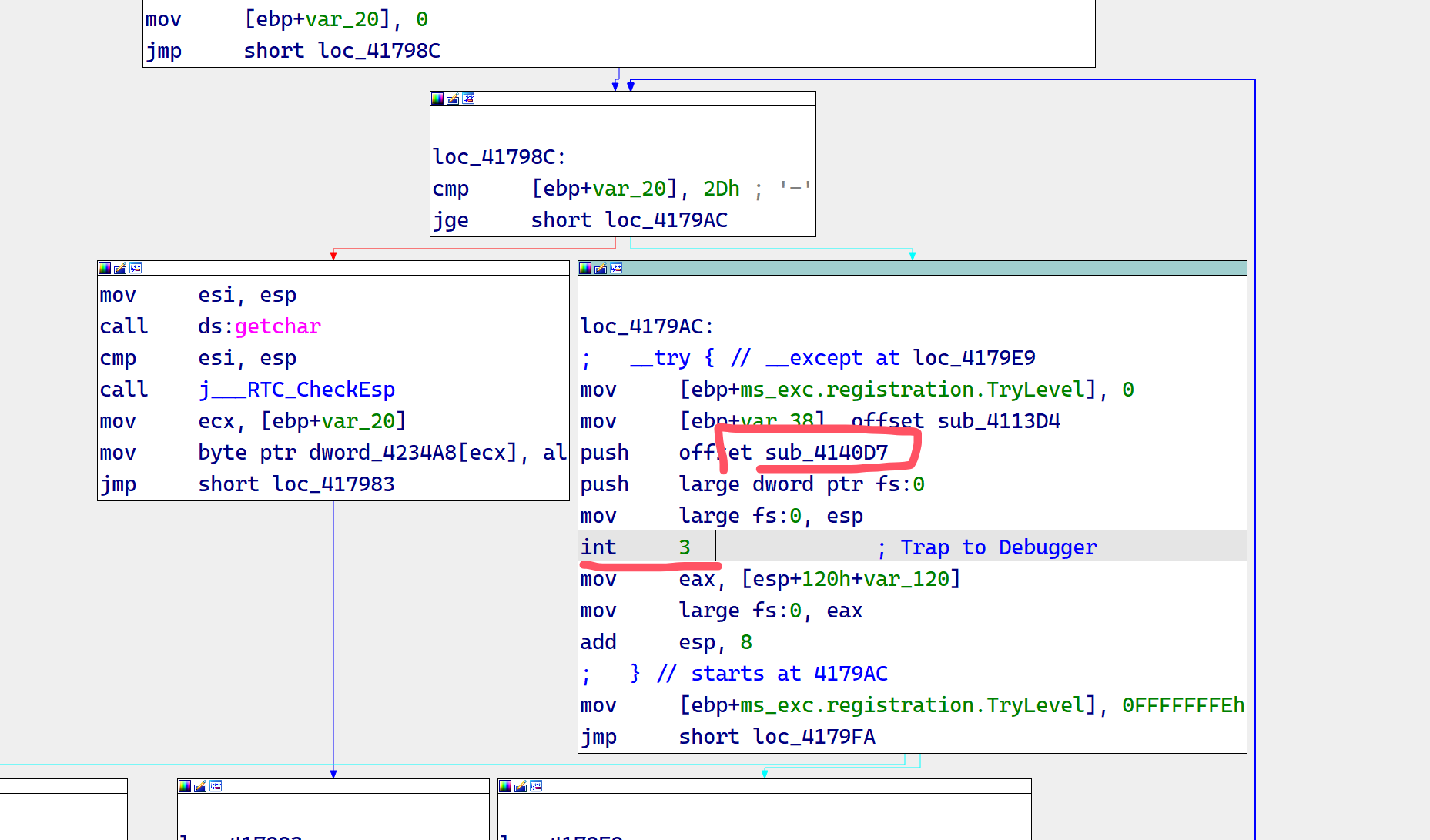
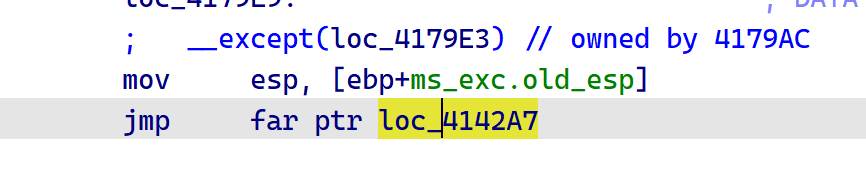
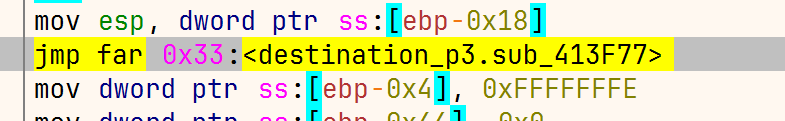
注意到是调用了check_23,并且这之前还有个简单加密
from z3 import Int, Solver
l = 30
a1 = [Int(f"x{i}") for i in range(l)]
s = Solver()
v1=a1[0]
v2=a1[1]
v3=a1[2]
v4=a1[3]
v5=a1[4]
v6=a1[5]
v7=a1[6]
v8=a1[7]
v10=a1[8]
v24=a1[9]
v25=a1[10]
v26=a1[11]
v27=a1[12]
v28=a1[13]
v29=a1[14]
v30=a1[15]
v31=a1[16]
v32=a1[17]
v33=a1[18]
v34=a1[19]
v35=a1[20]
v36=a1[21]
v37=a1[22]
v38=a1[23]
v39=a1[24]
v40=a1[25]
v20=a1[26]
v41=a1[27]
v22=a1[28]
s.add(255036*v7+-90989*v3+-201344*v4+122006*v5+-140538*v6+109859*v2-109457*v1-9396023 == 0)
s.add(277432*v6+110191*v3+-186022*v4+175123*v2-75564*v5-252340*v1-12226612 == 0)
s.add(127326*v4+260948*v2+-102835*v1+225038*v5-129683*v3-45564209 == 0)
s.add(-170345*v2+217412*v3-26668*v1+38500*v4-27440782 == 0)
s.add(25295*v2+69369*v3+191287*v1-24434293 == 0)
s.add(72265*v1-2384745 == 0)
s.add(264694*v1-190137*v2+19025100 == 0)
s.add(101752*v24+67154*v8+-20311*v1+-30496*v6+-263329*v7+-99420*v10+255348*v3+169511*v4-121471*v2+231370*v5-33888892 == 0)
s.add(17253*v8+-134891*v7+144501*v4+220594*v2+263746*v3+122495*v6+74297*v10+205480*v1-32973*v5-115484799 == 0)
s.add(251337*v3+-198187*v6+-217900*v2+-62192*v8+-138306*v7+-165151*v4-118227*v1-22431*v5+72699617 == 0)
s.add(243012*v27+-233931*v4+66595*v7+-273948*v5+-266708*v24+75344*v8-108115*v3-17090*v25+240281*v10+202327*v1-253495*v2+233118*v26+154680*v6+25687761 == 0)
s.add(41011*v8+-198187*v1+-117171*v7+-178912*v3+9797*v24+118730*v10-193364*v5-36072*v6+10586*v25-110560*v4+173438*v2-176575*v26+54358815 == 0)
s.add(-250878*v24+108430*v1+-136296*v5+11092*v8+154243*v7+-136624*v3+179711*v4+-128439*v6+22681*v25-42472*v10-80061*v2+34267161 == 0)
s.add(65716*v30+-18037*v26+-42923*v7+-33361*v4+161566*v6+194069*v25+-154262*v2+173240*v3-31821*v27-80881*v5+217299*v8-28162*v10+192716*v1+165565*v24+106863*v29-127658*v28-75839517 == 0)
s.add(-236487*v24+-45384*v1+46984*v26+148196*v7+15692*v8+-193664*v6+6957*v10+103351*v29-217098*v28+78149*v4-237596*v5-236117*v3-142713*v25+24413*v27+232544*v2+78860648 == 0)
s.add(-69129*v10+-161882*v3+-39324*v26+106850*v1+136394*v5+129891*v2+15216*v27+213245*v24-73770*v28+24056*v25-123372*v8-38733*v7-199547*v4-10681*v6+57424065 == 0)
s.add(-268870*v30+103546*v24+-124986*v27+42015*v7+80222*v2+-77247*v10+-8838*v25+-273842*v4+-240751*v28-187146*v26-150301*v6-167844*v3+92327*v8+270212*v5-87705*v33-216624*v1+35317*v31+231278*v32-213030*v29+114317949 == 0)
s.add(-207225*v1+-202035*v3+81860*v27+-114137*v5+265497*v30+-216722*v8+276415*v28+-201420*v10-266588*v32+174412*v6+249222*v24-191870*v4+100486*v2+37951*v25+67406*v26+55224*v31+101345*v7-76961*v29+33370551 == 0)
s.add(175180*v29+25590*v4+-35354*v30+-173039*v31+145220*v25+6521*v7+99204*v24+72076*v27+207349*v2+123988*v5-64247*v8+169099*v6-54799*v3+53935*v1-223317*v26+215925*v10-119961*v28-83559622 == 0)
s.add(43170*v3+-145060*v2+199653*v6+14728*v30+139827*v24+59597*v29+2862*v10+-171413*v31+-15355*v25-71692*v7-16706*v26+264615*v1-149167*v33+75391*v27-2927*v4-187387*v5-190782*v8-150865*v28+44238*v32-276353*v34+82818982 == 0)
s.add(-3256*v27+-232013*v25+-261919*v29+-151844*v26+11405*v4+159913*v32+209002*v7+91932*v34+270180*v10+-195866*v3-135274*v33-261245*v1+24783*v35+262729*v8-81293*v24-156714*v2-93376*v28-163223*v31-144746*v5+167939*v6-120753*v30-13188886 == 0)
s.add(-240655*v35+103437*v30+236610*v27+100948*v8+82212*v6+-60676*v5+-71032*v3+259181*v7+100184*v10+7797*v29+143350*v24+76697*v2-172373*v25-110023*v37-13673*v4+129100*v31+86759*v1-101103*v33-142195*v36+28466*v32-27211*v26-269662*v34+9103*v28-96428951 == 0)
s.add(-92750*v28+-151740*v27+15816*v35+186592*v24+-156340*v29+-193697*v2+-108622*v8+-163956*v5+78044*v4+-280132*v36-73939*v33-216186*v3+168898*v30+81148*v34-200942*v32+1920*v1+131017*v26-229175*v10-247717*v31+232852*v25+25882*v7+144500*v6+175681562 == 0)
s.add(234452*v34+-23111*v29+-40957*v2+-147076*v8+16151*v32+-250947*v35+-111913*v30+-233475*v24+-2485*v28+207006*v26+71474*v3+78521*v1-37235*v36+203147*v5+159297*v7-227257*v38+141894*v25-238939*v10-207324*v37-168960*v33+212325*v6+152097*v31-94775*v27+197514*v4+62343322 == 0)
s.add(-142909*v34+-111865*v31+258666*v36+-66780*v2+-13109*v35+-72310*v25+-278193*v26+-219709*v24+40855*v8+-270578*v38+96496*v5+-4530*v1+63129*v28-4681*v7-272799*v30-225257*v10+128712*v37-201687*v39+273784*v3+141128*v29+93283*v32+128210*v33+47550*v6-84027*v4+52764*v40-140487*v27+105279220 == 0)
s.add(216020*v38+-248561*v29+-86516*v33+237852*v26+-132193*v31+-101471*v3+87552*v25+-122710*v8+234681*v5+-24880*v7+-245370*v1+-17836*v36-225714*v34-256029*v4+171199*v35+266838*v10-32125*v24-43141*v32-87051*v30-68893*v39-242483*v28-12823*v2-159262*v27+123816*v37-180694*v6+152819799 == 0)
s.add(-116890*v3+67983*v27+-131934*v4+256114*v40+128119*v24+48593*v33+-41706*v2+-217503*v26+49328*v6+223466*v7+-31184*v5+-208422*v36+261920*v1+83055*v20+115813*v37+174499*v29-188513*v35+18957*v25+15794*v10-2906*v28-25315*v8+232180*v32-102442*v39-116930*v34-192552*v38-179822*v31+265749*v30-54143007 == 0)
s.add(-215996*v4+-100890*v40+-177349*v7+-159264*v6+-227328*v27+-91901*v24+-28939*v10+206392*v41+6473*v25+-22051*v20+-112044*v34+-119414*v30+-225267*v35+223380*v3+275172*v5+95718*v39-115127*v29+85928*v26+169057*v38-204729*v1+178788*v36-85503*v31-121684*v2-18727*v32+109947*v33-138204*v8-245035*v28+134266*v37+110228962 == 0)
s.add(-165644*v32+4586*v39+138195*v25+155259*v35+-185091*v3+-63869*v31+-23462*v30+150939*v41+-217079*v8+-122286*v6+5460*v38+-235719*v7+270987*v26+157806*v34+262004*v29-2963*v28-159217*v10+266021*v33-190702*v24-38473*v20+122617*v2+202211*v36-143491*v27-251332*v4+196932*v5-155172*v22+209759*v40-146511*v1+62542*v37+185928391 == 0)
s.add(57177*v24+242367*v39+226332*v31+15582*v26+159461*v34+-260455*v22+-179161*v37+-251786*v32+-66932*v41+134581*v1+-65235*v29+-110258*v28+188353*v38+-108556*v6+178750*v40+-20482*v25+127145*v8+-203851*v5+-263419*v10+245204*v33+-62740*v20+103075*v2-229292*v36+142850*v30-1027*v27+264120*v3+264348*v4-41667*v35+130195*v7+127279*a1[29]-51967523 == 0)
print(s.check())
m = s.model()
result = []
for i in a1:
result.append(m[i].as_long())
print(result)
ans = [105,244,63,10,24,169,248,107,129,138,25,182,96,176,14,89,56,229,206,19,23,21,22,198,179,167,152,66,28,201,213,80,162,151,102,36,91,37,50,17,170,41,3,84,85,226,131,38,71,32,18,142,70,39,112,220,16,219,159,222,11,119,99,203,47,148,185,55,93,48,153,113,1,237,35,75,67,155,161,74,108,76,181,233,186,44,125,232,88,8,95,163,200,249,120,243,174,212,252,234,58,101,228,86,109,144,104,121,117,87,15,132,12,20,165,115,136,135,118,69,68,2,82,123,250,251,53,255,51,221,211,195,145,140,254,0,116,43,29,217,197,183,168,188,34,218,146,147,98,149,246,180,103,33,40,207,208,192,143,26,154,225,100,141,175,124,230,62,177,205,110,202,253,173,46,52,114,164,166,137,158,122,13,83,178,133,189,187,7,184,77,245,216,190,194,72,157,172,171,199,160,45,49,27,204,81,6,92,59,209,239,130,97,61,214,215,73,90,126,42,30,240,79,224,78,223,111,60,4,5,196,231,106,64,139,235,150,227,238,191,127,31,156,54,241,242,134,247,128,65,94,57,210,236,9,193]
for i in range(l):
t = ans.index(result[i])
print(chr(t ^ 0xff ^ i), end='')
# flag{U_90t_th3_p1c5t0re_fl49!}主要是要注意下不能用BitVec,可能是因为有负数的运算吧。
RTTT
发现一个异或,出来结果是 Welc0me to RCTF 2O22
然后硬件断点一路跟下去,发现生成RC4的S盒。
然后拿到KeyStream(我的keystream是加密了'f'的结果)
然后对着结果硬件断点,发现一个strcmp。
不过我发现解出来后顺序不对,应该是有个树的遍历(看着比较像)
于是我弄了一个唯一确定的字符序列,用来获取SBox。
keystream = bytes.fromhex("""
11 93 47 0F 85 91 E1 FE 0C 8E 4D F8 6F 8A 87 CC
A4 7C 70 1B 09 96 30 26 5D 30 39 5E 43 BD 0F 81
09 74 B0 F4 4E 0B 90 63 48 11
""")
ans = bytes.fromhex("""
34 C2 65 2D DA C6 B1 AD 47 BA 06 A9 3B C1 CC D7
F1 29 24 39 2A C0 15 02 7E 10 66 7B 5E EA 5E D0
59 46 E1 D6 6E 5E B2 46 6B 31""")
k = [ans[i] ^ keystream[i] ^ ord('f') for i in range(len(keystream))]
t = "".join(map(chr, k))
print(k)
# generate SBOx
a = "yJzLkHwDxaCAtnsPipmIBfhljdGbeOqKNcEMugvFor"
b = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOP"
sbox = [a.index(b[i]) for i in range(len(a))]
for i in range(len(t)):
print(t[sbox[i]], end='') # RCTF{03C3E9B2-E37F-2FD6-CD7E-57C91D77DD61}CheckYourKey
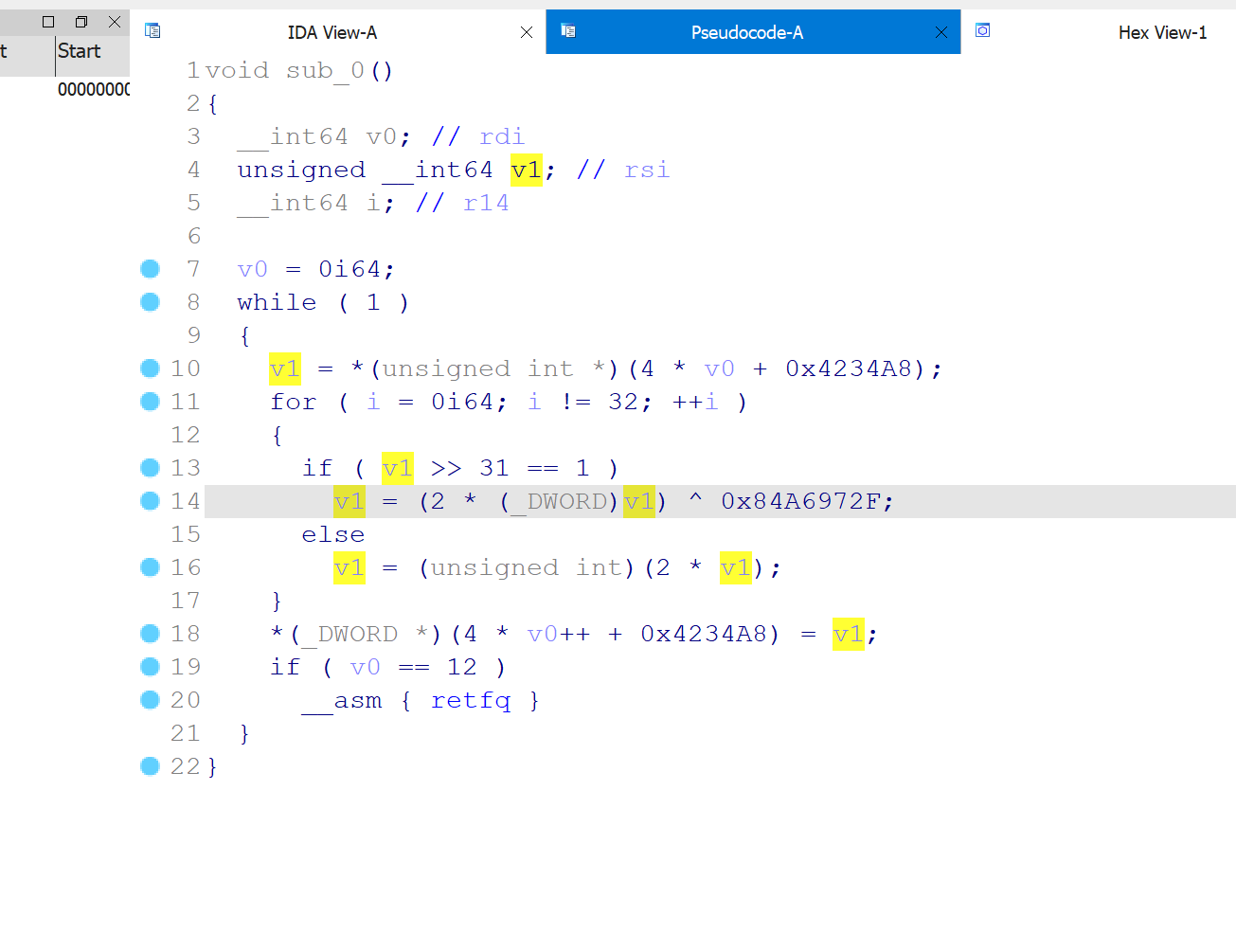
RegisterNatives -> True Function -> AES -> B58Encode(table1) -> B64Encode(table2) -> Strcmp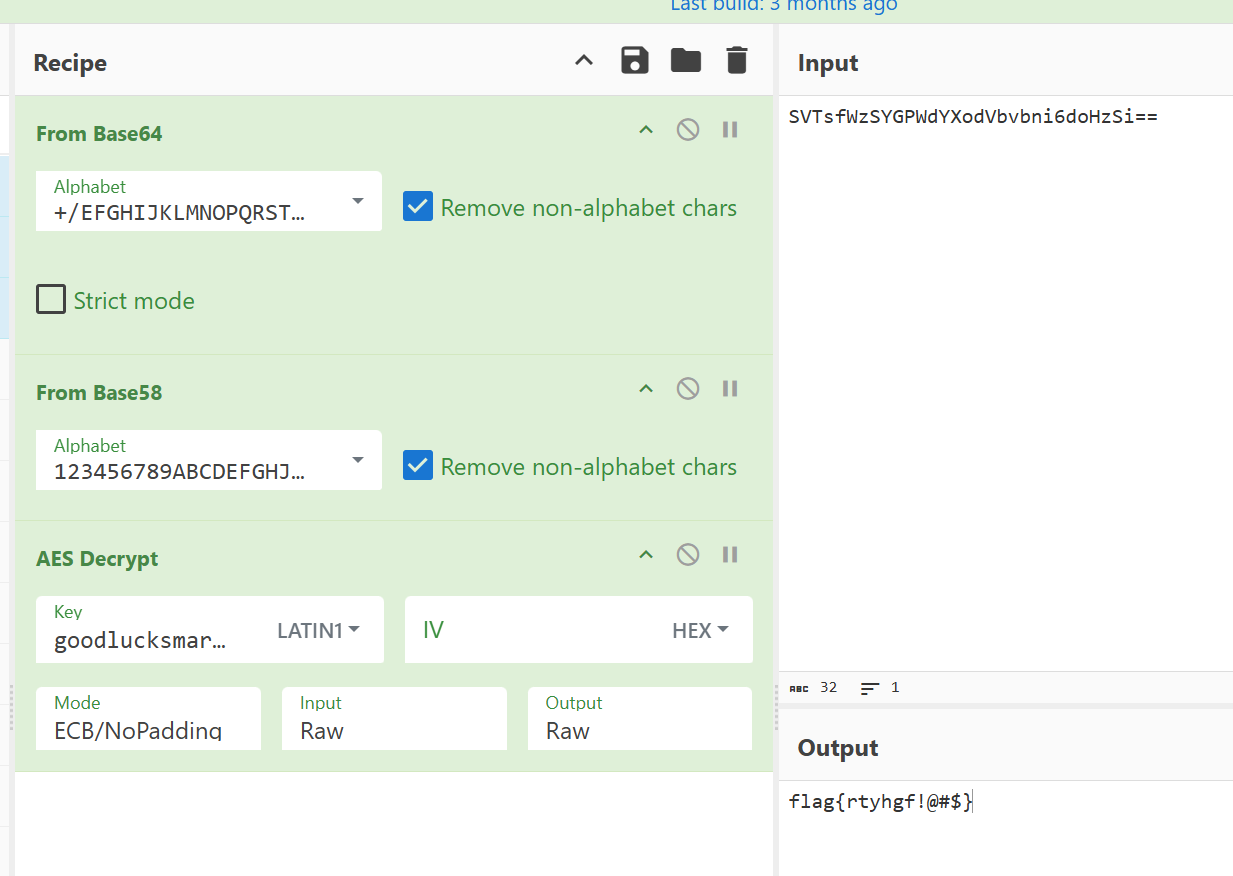
web_run
JEB 反编译,找到main函数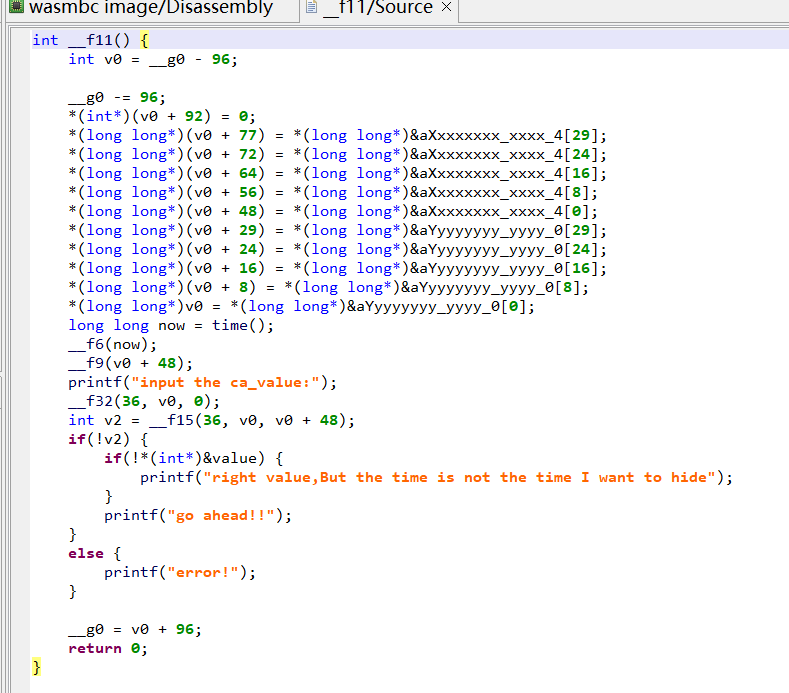
SEED = (202211110054 - 1) & 0xffffffff
def _f7():
global SEED
v0 = SEED * 6364136223846793005 + 1
SEED = v0
return (v0 >> 33) % 16
def _f8(par):
if par >= 0 and par <= 9:
return 48 + par
val = par - 10
if val == 0:
return 97
elif val == 1:
return 98
elif val == 2:
return 99
elif val == 3:
return 100
elif val == 4:
return 101
elif val == 5:
return 102
return 48
def generate(s):
for i in range(len(s)):
if not (s[i] != 52 and s[i] != 45):
continue
if s[i] == 120:
v2 = _f8(_f7())
s[i] = v2
else:
v2 = _f8((_f7() & 3) | 0x8)
s[i] = v2
return bytes(s)
A = generate(list(b'xxxxxxxx-xxxx-4xxx-yxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx'))
print(f"RCTF{{{A.decode()}}}")
# RCTF{40959ea7-26e0-4c9d-8f4a-62faf14ff392}